The AI-ALOE researchers and scientists have developed and deployed a suite of AI technologies in classes to help create engaging and personalized learning experiences, driving educational innovation at scale.
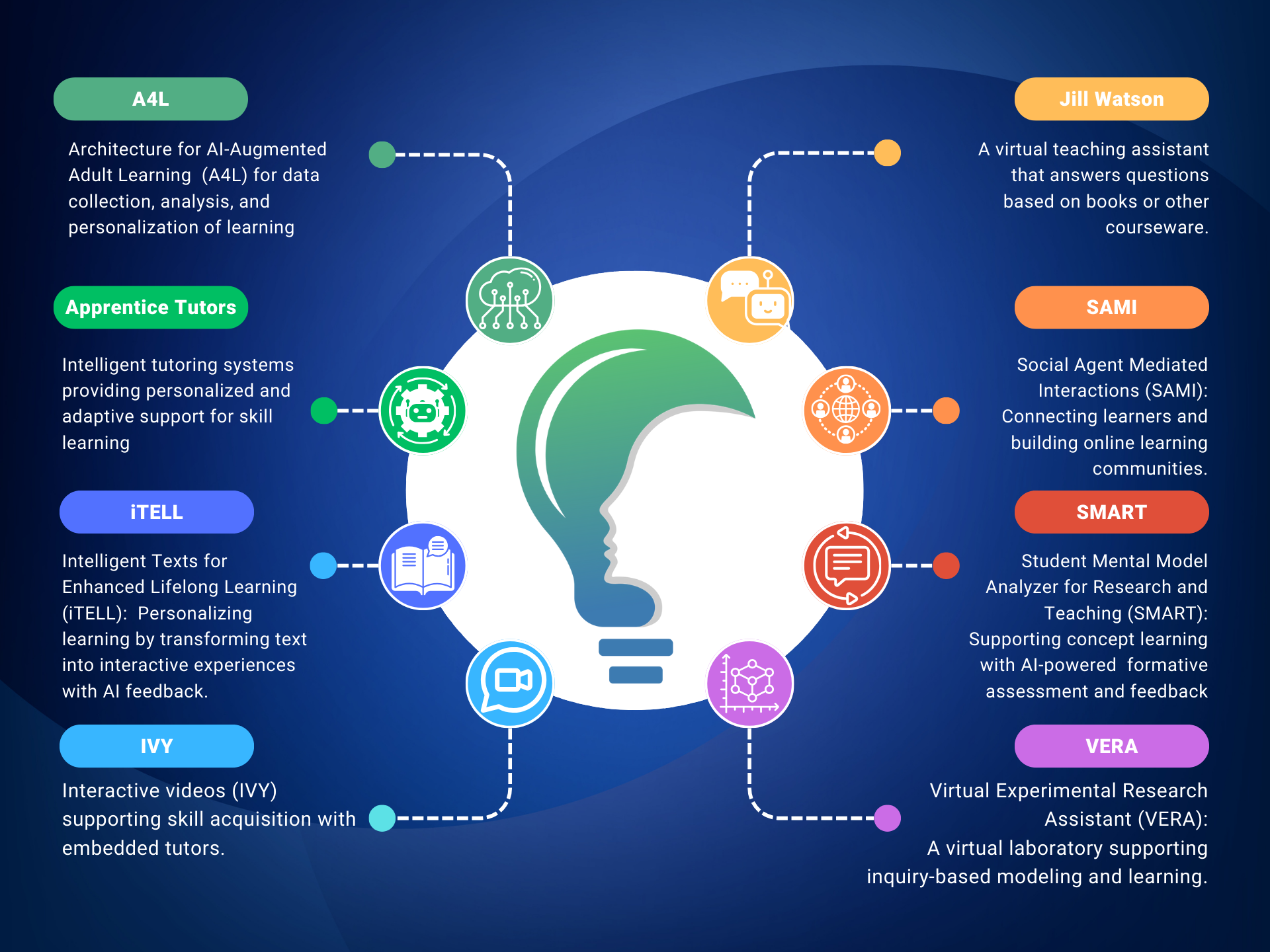
You can learn more about these technologies from the summary below on how they help address teaching and learning challenges. You can also watch a short video demonstrating how each technology works.
We continue improving these technologies and developing new capabilities based on the feedback from teachers and students who are using them in teaching and learning. We are also looking for opportunities to expand their applications in more classes in various disciplines. Please contact us if you are interested in partnering with us to integrate these technologies into your curriculum.
Apprentice Tutors
An Intelligent Tutoring System Providing Personalized and Adaptive Support for
Math Problem Solving and Skill Learning
iTELL
An Intelligent Framework That Personalizes Learning by
Transforming Traditional Text into Interactive Experiences with AI Feedback
Ivy
Intelligent AI Coach by Georgia Tech’s Design Intelligence Lab Enhances Online Learning for Adult Re-Skilling/Up-Skilling
- Skill Learning: Understanding and Explaining Skills (Ivy) PowerPoint
- Ivy: Foundations and Architecture
Jill Watson
A Virtual Teaching Assistant That Empowers Teachers to Support and Engage All Students
SAMI (Social Agent Mediated Interactions)
An AI Agent Connecting Learners and Building Community in Online Learning
SMART (Student Mental Model Analyzer for Research and Teaching)
An AI-Powered System for Formative Assessment and Feedback
VERA (Virtual Experimentation Research Assistant)

